側欄
這是本文件的舊版!
目錄表
Git 說明
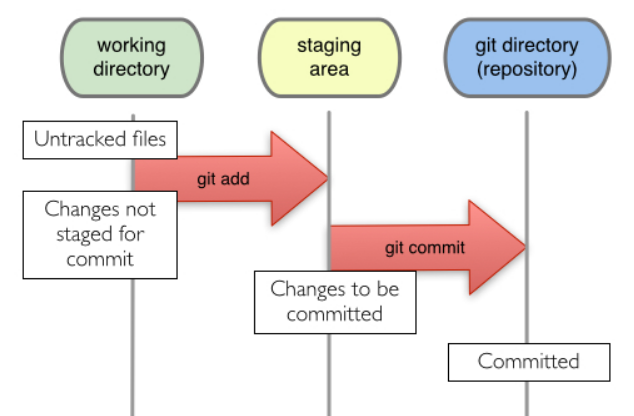
一個 Git 目錄裡,可以分成三種區域:
• 目前工作目錄 Working tree • 暫存準備遞交區 Staging Area • 儲存庫 Repository
Git 是分散式的版本控制系統, 從架設、簡易操作、設定, 此篇主要是整理 基本操作、遠端操作 等.
你有兩種主要方法來取得一個 Git 倉儲。
第一種是將現有的專案或者資料夾匯入 Git;
第二種是從其它伺服器克隆(clone)一份現有的 Git 倉儲。
Git clone
Git clone 取得現有 Git repository 副本。
Git 並不僅只是取得專案最新的內容,而是把遠端倉儲內幾乎所有的資料都抓回來了。
專案歷史紀錄中,每個檔案的每個版本預設都會在你執行 git clone 時被拉取(pull)回來。
注意現在這個命令是克隆(clone),而非取出(checkout)。
這是 Git 和其他版本控制系統的重要差異。
git clone https://github.com/libgit2/libgit2
這指令將會建立名為「libgit2」的資料夾,並在這個資料夾下初始化一個 .git 資料夾,從遠端倉儲拉取所有資料,並且取出(checkout)專案中最新的版本。
git clone https://github.com/libgit2/libgit2 mylibgit
這個命令做的事與上一個命令大致相同,只不過在本地創建的倉庫名字變為 mylibgit。
Git submodule
Git submodule 功能就是建立了當前項目與子模塊之間的依賴關係。
git submodule add <repository> [<path>] git submodule init
#根據 .gitmodules 的名稱和 URL,將這些資訊註冊到 .git/config (也就是主要的 REPO) 內,可是把 .gitmodules 內不用的 submodule 移除,使用這個指令並沒辦法自動刪除 .git/config 的相關內容,必須手動刪除;
git submodule update
#根據已註冊(也就是 .git/config )的 submodule 進行更新,例如 clone 遺失的 submodule,也就是上一段講的方法,所以執行這個指令前最好加上 –init;
git submodule sync
#如果 submodule 的 remote URL 有變動,可以在 .gitmodules 修正 URL,然後執行這個指令,便會將 submodule 的 remote URL 更正。
Git init
Git init 建立新的 repository
初始化一個新的 repository
這個命令將會建立一個名為 .git 的子資料夾,其中包含 Git 所有必需的倉儲檔案,也就是 Git 倉儲的骨架。
注意事項
由 project/.git/config 可知: (若有更多, 亦可由此得知)
origin(remote) 是 Repository 的版本 master(branch) 是 local 端, 正在修改的版本
平常沒事不要去動到 origin, 如果動到, 可用 git reset –hard 回覆到沒修改的狀態.
Git add
Git add 新增檔案。
• git add . # 將資料先暫存到 staging area, add 之後再新增的資料, 於此次 commit 不會含在裡面. • git add filename • git add modify-file # 修改過的檔案, 也要 add. (不然 commit 要加上 -a 的參數) • git add -u # 只加修改過的檔案, 新增的檔案不加入. • git add -i # 進入互動模式
Git rm
Git rm 刪除檔案。
git rm filename
Git mv
Git mv 修改檔名、搬移目錄。
git mv filename new-filename
Git clean
Git clean 砍掉 untracked 檔案。
git clean -n # 列出打算要清除的檔案 git clean -f # 真的清除 git clean -x # 連 gitignore 裡列的檔案也清掉
Git status
Git status 看目前的狀態。
git status # 看目前檔案的狀態 git status HEAD # 與 HEAD 所指的 Commit 做比對
Git commit
Git commit 主要是將暫存區裡的改動提交到本地的版本庫。
git commit git commit -m 'commit message' git commit -a -m 'commit -message' # 將所有修改過得檔案都 commit, 但是 新增的檔案 還是得要先 add. git commit -a -v # -v 可以看到檔案哪些內容有被更改, -a 把所有修改的檔案都 commit git commit --amend # 變更修改當前的提交
Git branch
Git branch 產生新的 branch。
git branch # 列出目前有多少 branch git branch new-branch # 產生新的 branch (名稱: new-branch), 若沒有特別指定, 會由目前所在的 branch / master 直接複製一份. git branch new-branch master # 由 master 產生新的 branch(new-branch) git branch new-branch v1 # 由 tag(v1) 產生新的 branch(new-branch) v1 為一個特定的 COMMIT ID (SHA-1) 哈希值 git branch -d new-branch # 刪除 new-branch git branch -D new-branch # 強制刪除 new-branch 如過分支還沒合併,則要使用強制刪除。 git branch -m old_brabch_name new_branch_name # 更改 branch name git checkout -b new-branch test # 產生新的 branch, 並同時切換過去 new-branch # 與 remote repository 有關 git branch -r # 列出所有 Repository branch git branch -a # 列出所有 branch
Git checkout
Git checkout 切換 branch。
• git checkout branch-name # 切換到 branch-name • git checkout master # 切換到 master • git checkout -b new-branch master # 從 master 建立新的 new-branch, 並同時切換過去 new-branch • git checkout -b newbranch # 由現在的環境為基礎, 建立新的 branch • git checkout -b newbranch origin # 於 origin 的基礎, 建立新的 branch • git checkout filename # 還原檔案到 Repository v • git checkout HEAD . # 將所有檔案都 checkout 出來(最後一次 commit 的版本), 注意, 若有修改的檔案都會被還原到上一版. (git checkout -f 亦可) • git checkout xxxx . # 將所有檔案都 checkout 出來(xxxx commit 的版本, xxxx 是 commit 的編號前四碼), 注意, 若有修改的檔案都會被還原到上一版. • git checkout -- * # 恢復到上一次 Commit 的狀態(* 改成檔名, 就可以只恢復那個檔案) • git checkout . # 編輯檔案後,恢復目錄到最後一次的 commit 狀態 • git checkout [FileName] # 把某支修改過的檔案還原到未修改狀態 commit 後修改的檔案內容移除
Git diff
Git diff 在 Git 中比對兩個版本之間的差異。
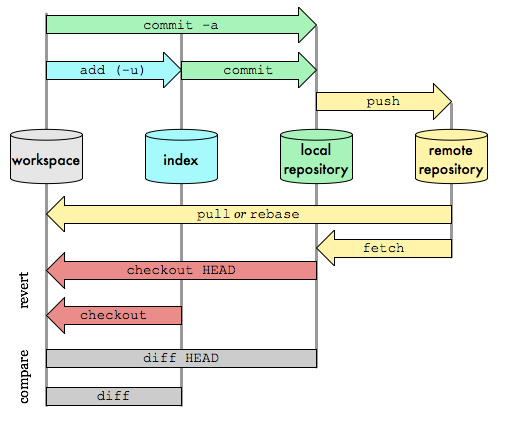
git diff master # 與 Master 有哪些資料不同 git diff --cached # 比較 staging area 跟本來的 Repository git diff tag1 tag2 # tag1, 與 tag2 的 diff git diff tag1:file1 tag2:file2 # tag1, 與 tag2 的 file1, file2 的 diff git diff # 比較 目前位置 與 staging area git diff --cached # 比較 staging area 與 Repository 差異 git diff HEAD # 比較目前位置 與 Repository 差別 git diff new-branch # 比較目前位置 與 branch(new-branch) 的差別 git diff --stat git diff:是查看 workspace 与 index(Staging Area) 的差别的。 git diff --cached:是查看 index(Staging Area) 与 local repositorty 的差别的。 git diff HEAD:是查看 workspace 和 local repository 的差别的。 (HEAD 指向的是 local repository 中最新提交的版本) cd /d c:\edk2 git checkout tags/edk2-stable202005 -b edk2-stable202005
Git cherry-pick
Git cherry-pick 只把某一其他分支的 commit 套用到進特定分支。
git cherry-pick <commit-hash> # 只把某一其他分支的 commit 套用到進 master 分支 git cherry-pick <hash-a> <hash-b> # 一次轉移其他分支中的多個 commit 進 master 分支 git cherry-pick <hash-a>..<hash-b> # 一次轉移一連串的 commit 進 master 分支 git cherry-pick <branch-name> # 把該分支的最後一次 commit 套的到 master 分支
Git tag
Git tag 列出 Git 中所有標籤。
git tag v1 ebff # log 是 commit ebff810c461ad1924fc422fd1d01db23d858773b 的內容, 設定簡短好記得 Tag: v1 git tag 中文 ebff # tag 也可以下中文, 任何文字都可以 git tag -d 中文 # 把 tag=中文 刪掉
Git log
Git log 命令只能查看以當前狀態為終點的歷史日誌。
• git log # 將所有 log 秀出 • git log --all # 秀出所有的 log (含 branch) • git log -p # 將所有 log 和修改過得檔案內容列出 • git log -p filename # 將此檔案的 commit log 和 修改檔案內容差異部份列出 • git log --name-only # 列出此次 log 有哪些檔案被修改 • git log --stat --summary # 查每個版本間的更動檔案和行數 • git log filename # 這個檔案的所有 log • git log directory # 這個目錄的所有 log • git log -S'foo()' # log 裡面有 foo() 這字串的. • git log --no-merges # 不要秀出 merge 的 log • git log --since="2 weeks ago" # 最後這 2週的 log • git log --pretty=oneline # 秀 log 的方式,選項將每一個更新印到單獨一行。 • git log --pretty=short # 秀 log 的方式 • git log --pretty=format:'%h was %an, %ar, message: %s' • git log --pretty=format:'%h : %s' --graph # 會有簡單的文字圖形化, 分支等. • git log --pretty=format:'%h : %s' --topo-order --graph # 依照主分支排序 • git log --pretty=format:'%h : %s' --date-order --graph # 依照時間排 • git log --stat # 列出被更動的檔案、有多少檔案被更動,以及有多行列被加入或移出該檔案。
Git reflog
Git reflog 可以叫做顯示可引用的歷史版本紀錄。
• git reflog # 查看當前倉庫的操作日誌,連修改 amend 都會有紀錄
Git show
Git show 顯示最新的一版的異動。
• git show ebff # 查 log 是 commit ebff810c461ad1924fc422fd1d01db23d858773b 的內容 • git show v1 # 查 tag:v1 的修改內容 • git show v1:test.txt # 查 tag:v1 的 test.txt 檔案修改內容 • git show HEAD # 此版本修改的資料 • git show HEAD^ # 前一版修改的資料 • git show HEAD^^ # 前前一版修改的資料 • git show HEAD~4 # 前前前前一版修改的資料
Git reset
Git reset 還原。
• git reset --hard HEAD # 還原到 HEAD所指的 commit ID • git reset master^ # 還原到 Master所指的 commit ID再往前一個 commit • git reset --hard HEAD^ # 還原到 HEAD所指的 commit ID再往前一個 commit • git reset --hard HEAD~3 # 還原到 HEAD所指的 commit ID再往前三個 commit,也等於 git reset --hard HEAD ^^^ • git reset --soft HEAD~3 • git reset HEAD filename # 從 staging area 狀態回到 unstaging 或 untracked (檔案內容並不會改變) • git reset --hard COMMIT ID(SHA-1) 哈希值只要輸入4位以上就可執行
| 模式 | mixed 模式 | soft 模式 | hard 模式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工作目錄 | 不變 | 不變 | 丟掉 |
| 暫存區 | 丟掉 | 不變 | 丟掉 |
Git revert
Git revert 資料還原。
• git revert HEAD # 回到前一次 commit 的狀態 • git reset HEAD filename # 從 staging area 狀態回到 unstaging 或 untracked (檔案內容並不會改變) • git checkout filename # 從 unstaging 狀態回到最初 Repository 的檔案(檔案內容變回修改前) • git revert HEAD --no-edit # 還原HEAD所指的 commit ID,並不是直接刪除,而是另外加上一個 commit ,加上後面的 --no-edit 參數,表示不編輯 Commit 訊息。 呈現的會是 Revert "commit remark"
| 指令 | 改變歷史紀錄 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
| Reset | 是 | 把目前的狀態設定成某個指定的 Commit 的狀態,通常適用於尚未推出去的 Commit。 |
| Rebase | 是 | 不管是新增、修改、刪除 Commit 都相當方便,用來整理、編輯還沒有推出去的 Commit 相當方便,但通常也只適用於尚未推出去的 Commit。 |
| Revert | 否 | 新增一個 Commit 來反轉(或說取消)另一個 Commit 的內容,原本的 Commit 依舊還是會保留在歷史紀錄中。雖然會因此而增加 Commit 數,但通常比較適用於已經推出去的 Commit,或是不允許使用 Reset 或 Rebase 之修改歷史紀錄的指令的場合。 |
Git grep
Git grep 尋找。
• git grep "te" v1 # 查 v1 是否有 "te" 的字串 • git grep "te" # 查現在版本是否有 "te" 的字串
Git stash
Git stash 暫存。
• git stash # 丟進暫存區 • git stash list # 列出所有暫存區的資料 • git stash pop # 取出最新的一筆, 並移除. • git stash apply # 取出最新的一筆 stash 暫存資料. 但是 stash 資料不移除 • git stash clear # 把 stash 都清掉
Git merge
Git merge 合併。
• git merge • git merge master • git merge new-branch
下述轉載自: ihower 的 Git 版本控制系統(2) 開 branch 分支和操作遠端 repo.x
• Straight merge 預設的合併模式,會有全部的被合併的 branch commits 記錄加上一個 merge-commit,看線圖會有兩條 Parents 線,並保留所有 commit log。
• Squashed commit 壓縮成只有一個 merge-commit,不會有被合併的 log。SVN 的 merge 即是如此。
• cherry-pick 只合併指定的 commit
• rebase 變更 branch 的分支點:找到要合併的兩個 branch 的共同的祖先,然後先只用要被 merge 的 branch 來 commit 一遍,然後再用目前 branch 再 commit 上去。這方式僅適合還沒分享給別人的 local branch,因為等於砍掉重練 commit log。
指令操作 • git merge <branch_name> # 合併另一個 branch,若沒有 conflict 衝突會直接 commit。若需要解決衝突則會再多一個 commit。 • git merge --squash <branch_name> # 將另一個 branch 的 commit 合併為一筆,特別適合需要做實驗的 fixes bug 或 new feature,最後只留結果。合併完不會幫你先 commit。
Git cherry-pick
Git cherry-pick 合併單一的 commit。
• git cherry-pick <commit ID> f # 只合併特定其中一個 commit。如果要合併多個,可以加上 -n 指令就不會先幫你 commit,這樣可以多 pick 幾個要合併的 commit,最後再 git commit 即可。
Git blame
Git blame 可以看到檔案的每一行是誰修改的。
• git blame filename # 關於此檔案的所有 commit 紀錄
Git am
Git am 對於 format-patch 製作的新式補丁,應當使用 git am 命令。
• git am --abort # 放棄更新 • git am --skip • git am --resolved • git am ~/patch-set/*.patch # 打上家用目錄的指定目錄下所有檔案 PATCH • git-am ../patch/0001-trival-patch.patch # 打上上一層目錄下的單一檔案 PATCH • git-am ~/patch/0001-trival-patch.patch # 打上家用目錄下的單一檔案 PATCH • Fixed patch Error Step: • git am ../patch/*.patch • git apply PATCH --reject • vim none_fixed files • git add fixed files • git am --resolved
Git apply
Git apply 是 git 中的 patch 命令。
• git apply PATCH --reject • git apply --reject 0001-XXX.patch • git status # 可以檢查有多少 rej 檔案產生,再逐一修正。
Git ls-files
Git ls-files 還原已被刪除的檔案。
• git ls-files -d # 查看已刪除的檔案 • git ls-files -d | xargs git checkout -- # 將已刪除的檔案還原
Git gc
Git gc 維護。
• git gc # 整理前和整理後的差異, 可由: git count-objects 看到. • git gc --prune • git fsck --full
Git rollback
Git Rollback 還原到上一版。
• git reset --soft HEAD^ • 編輯 + git add filename • git commit -m 'rollback'
Git remote
以下與 遠端 Repository 相關 Git remote 維護遠端檔案。
• git remote • git remote add new-branch http://git.example.com.tw/project.git # 增加遠端 Repository 的 branch(origin -> project) • git remote show # 秀出現在有多少 Repository • git remote rm new-branch # 刪掉 • git remote update # 更新所有 Repository branch • git branch -r # 列出所有 Repository branch $git remote origin --> 它是 Git 給定的預設簡稱,用來代表被克隆的來源。 $ git remote -v origin https://github.com/schacon/ticgit (fetch) origin https://github.com/schacon/ticgit (push) $git fetch origin --> origin就代替上述的網址 $git push origin --> origin就代替上述的網址
Git fetch
Git fetch 抓取 / 切換 Repository 的 branch。
• git fetch origin • git checkout --track -b reps-branch origin/reps-branch # 抓取 reps-branch, 並將此 branch 建立於 local 的 reps-branch
Git push
Git push 推送到遠端的 Repository。
• git push [remote-name] [branch-name] 只有在你對克隆來源的伺服器有寫入權限,並且在這個當下還沒有其它人推送過,這個命令才會成功; 如果你和其它人同時做了克隆,然後他們先推送到上游,接著換你推送到上游,毫無疑問地你的推送會被拒絕; 你必需先獲取他們的工作內容,將其整併到你之前的工作內容,如此你才會被允許推送。 刪除 Repository 的 branch • git push origin :heads/reps-branch • git push origin --delete reps-branch